Creating A Build Tool Using Go
Part of Daniel Katungi’s talk during Daytona Developers Club Tour ‘24, Nairobi on Thurdsay July 18th
Understanding a fully-fledged web build tool(Vite)
Vite is a frontend build tool that has revolutionized the development experience by leveraging native ESM capabilities of modern browsers. To fully grasp its power. Core concepts:
- Native ESM
- Leveraging Browser Capabilities: Vite takes advantage of the native ESM (EcmaScript Modules) support in modern browsers. It can serve you code directly as ESM modules without the need for bundling during development.
- Improved Development Experience: This approach significantly speeds up development because the browser handles module loading efficiently.
- Why Vite
- Bundle Up? Vite or Webpack?
- ESBuild
- High-Performance Builder: Vite utilizes ESBuild, a Go-based bundler, for production builds. ESBuild is renowned for its incredible speed and efficiency.
- Optimized Output: It produces highly optimized bundles, resulting in faster load times for your application.
- Getting started with Vite
- Dependency Pre-Bundling
- Optimized Import Paths: Vite pre-bundles large dependency libraries into chunks to reduce the number of requests and improve load performance.
- Faster Development: This optimization helps in faster development by avoiding unnecessary re-bundling during development.
- Dependency Pre-Bundling
- Hot Module Replacement (HMR)
- Instant Updates: Vite implements HMR to enable rapid development by updating only the changed modules in the browser without a full page reload.
- Improved Developer Experience: This significantly enhances the development workflow by providing instant feedback on code changes.
- Plugin System
- Extensibility: Vite offers a flexible plugin system that allows developers to customize the build process to fit their specific needs.
- Rich Ecosystem: There’s a vast ecosystem of Vite plugins available for various tasks like TypeScript support, CSS preprocessors, and more.
- The Ultimate Guide to Using Vite Plugin for Lightning-Fast Web Development
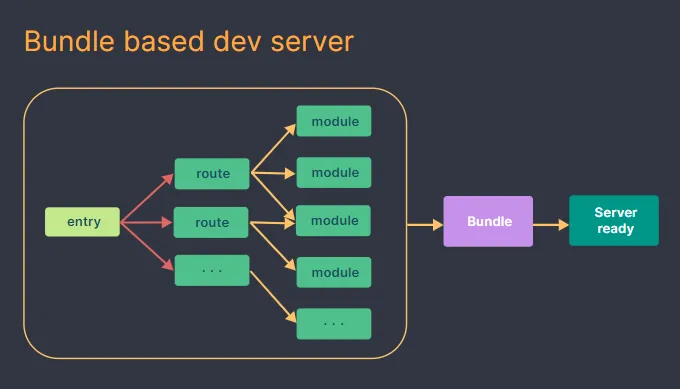
How It Works
- Development Server: Vite starts a development server that serves your code directly as ESM modules. The browser handles module imports efficiently.
- HMR: Vite watches for changes in your code and uses WebSockets to send updates to the browser.1 Only the affected modules are reloaded, providing a fast feedback loop. Vite In The Browser Vite Core Features
- Production Build: When building for production, Vite uses ESBuild to bundle your code into optimized chunks. Dependency pre-bundling is applied to further improve performance.
“Vite isn’t just a fast bundler, it’s a development powerhouse. Native ESM support and Hot Module Replacement (HMR) dramatically accelerate your development workflow, while ESBuild and dependency pre-bundling ensure your production builds fly.”
Creating a Build Tool Using Go
- Set Up Your Go Environment:
- Install Go from the official Go website.
- Create a new Go project directory.
- Install Dependencies:
- Run the following commands to install the
minifypackage and its sub-packages for JavaScript and CSS minification:go get -u github.com/tdewolff/minify go get -u github.com/tdewolff/minify/js go get -u github.com/tdewolff/minify/css
- Run the following commands to install the
- Read and Parse Files:
- Use the
osandio/ioutilpackages to read files from the filesystem.
- Use the
- Transpile, Bundle, and Minify Code:
- Use the
minifypackage to minify JavaScript and CSS files. - Bundle multiple JavaScript and CSS modules into a single file.
- Use the
- Serve Files:
- Use the
net/httppackage to serve files during development. - Implement a simple server that watches for file changes and reloads the browser.
- Use the
- Command-Line Interface (CLI):
- Create a CLI using the
flagpackage to provide options for building, serving, and watching files.
- Create a CLI using the
Here is the complete code for the build tool:
package main
import (
"flag"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
"os"
"path/filepath"
"strings"
"github.com/tdewolff/minify"
"github.com/tdewolff/minify/css"
"github.com/tdewolff/minify/js"
)
func main() {
// Define CLI flags
build := flag.Bool("build", false, "Build the project")
serve := flag.Bool("serve", false, "Serve the project")
flag.Parse()
if *build {
buildProject()
}
if *serve {
serveProject()
}
}
func buildProject() {
// Initialize minifier
m := minify.New()
m.AddFunc("text/javascript", js.Minify)
m.AddFunc("text/css", css.Minify)
// Read and concatenate JavaScript and CSS files
files, err := ioutil.ReadDir("./src")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error reading source directory:", err)
return
}
var bundledCode strings.Builder
for _, file := range files {
content, err := ioutil.ReadFile("./src/" + file.Name())
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error reading file:", err)
return
}
var minifiedContent string
if strings.HasSuffix(file.Name(), ".js") {
minifiedContent, err = m.String("text/javascript", string(content))
} else if strings.HasSuffix(file.Name(), ".css") {
minifiedContent, err = m.String("text/css", string(content))
}
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error minifying file:", err)
return
}
bundledCode.WriteString(minifiedContent)
}
// Ensure the dist directory exists
err = os.MkdirAll("./dist", os.ModePerm)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error creating dist directory:", err)
return
}
// Write the bundled and minified code to a file
err = ioutil.WriteFile("./dist/bundle.js", []byte(bundledCode.String()), 0644)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error writing bundled file:", err)
} else {
fmt.Println("Project built successfully.")
}
}
func serveProject() {
http.Handle("/", http.FileServer(http.Dir("./dist")))
fmt.Println("Serving project at http://localhost:8080")
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil)
}
Steps to Use the Build Tool
- Build the Project:
go run main.go -build - Serve the Project:
go run main.go -serve
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: